Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 Founders Edition Review
Every couple of years, Nvidia unleashes a powerhouse of a graphics card, pushing PC gaming into a new era. The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 is that card, but its approach to next-gen performance is unique. In many games, the performance boost over the RTX 4090 isn't as dramatic as expected—at least without DLSS Frame Generation. However, the next generation of Nvidia's DLSS, for both upscaling and frame generation, delivers incredible leaps in image quality and performance, exceeding typical generational improvements.
The RTX 5090's upgrade value depends on your games, resolution, and tolerance for AI-generated frames. For those with monitors below 4K 240Hz, this upgrade might not be worthwhile. But for high-end display owners, the AI-generated frames offer a glimpse into the future of gaming.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 – Photos
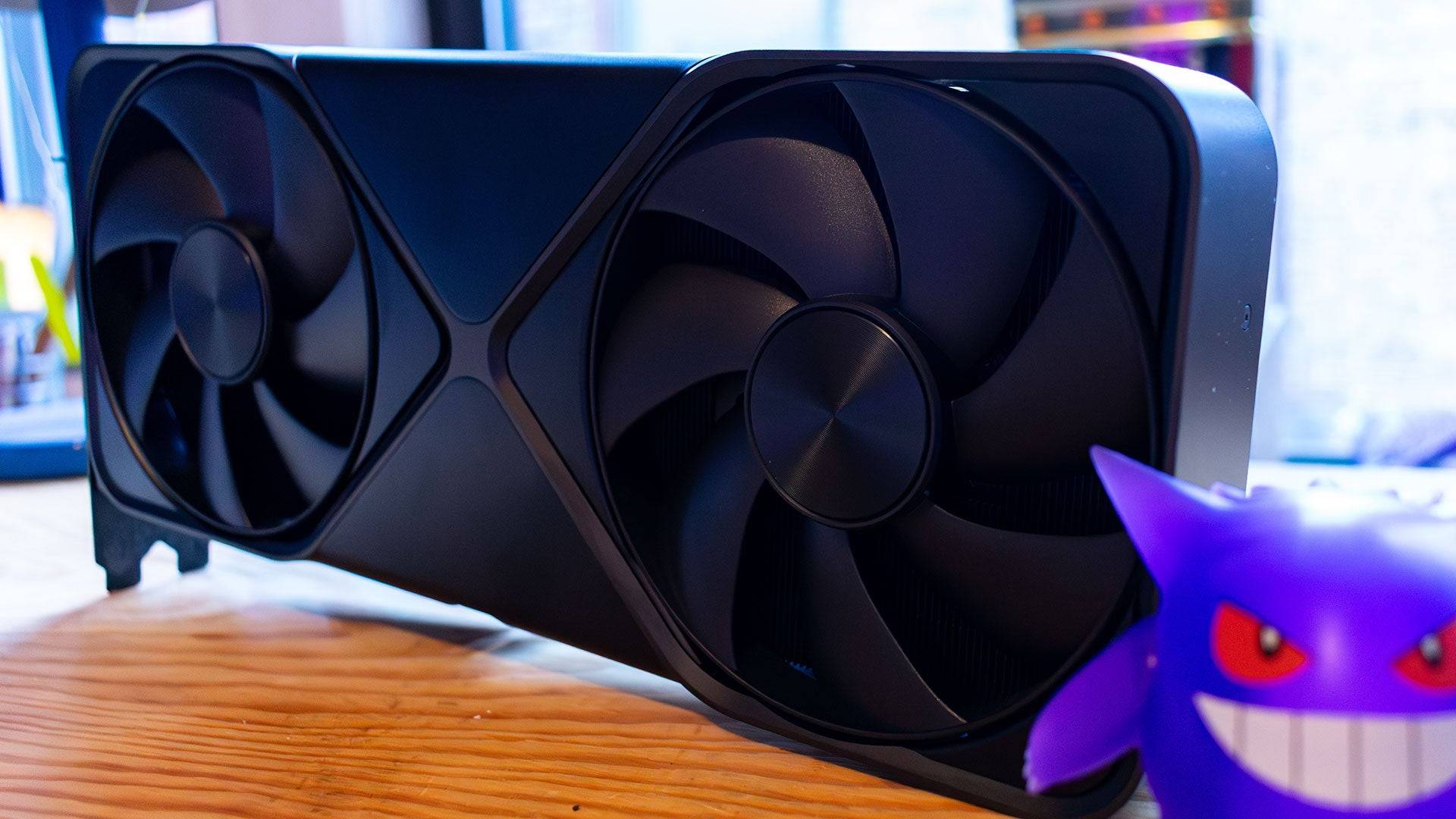





RTX 5090 – Specs and Features
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 uses Blackwell, Nvidia's high-end architecture powering many popular AI models. This hints at the 5090's strengths, but Nvidia didn't ignore non-AI aspects. The 5090 packs more Streaming Multiprocessors (SMs) into the same Graphics Processing Clusters (GPCs), resulting in 21,760 CUDA cores—a 32% increase over the RTX 4090. This boosts raw gaming performance.
Each SM boasts four Tensor Cores and one RT Core, like its predecessor. This equates to 680 Tensor Cores and 170 RT cores, compared to the RTX 4090's 512 and 128, respectively. The 5th-generation Tensor Cores are designed for enhanced AI performance, adding FP4 support to reduce VRAM dependency in AI workloads.

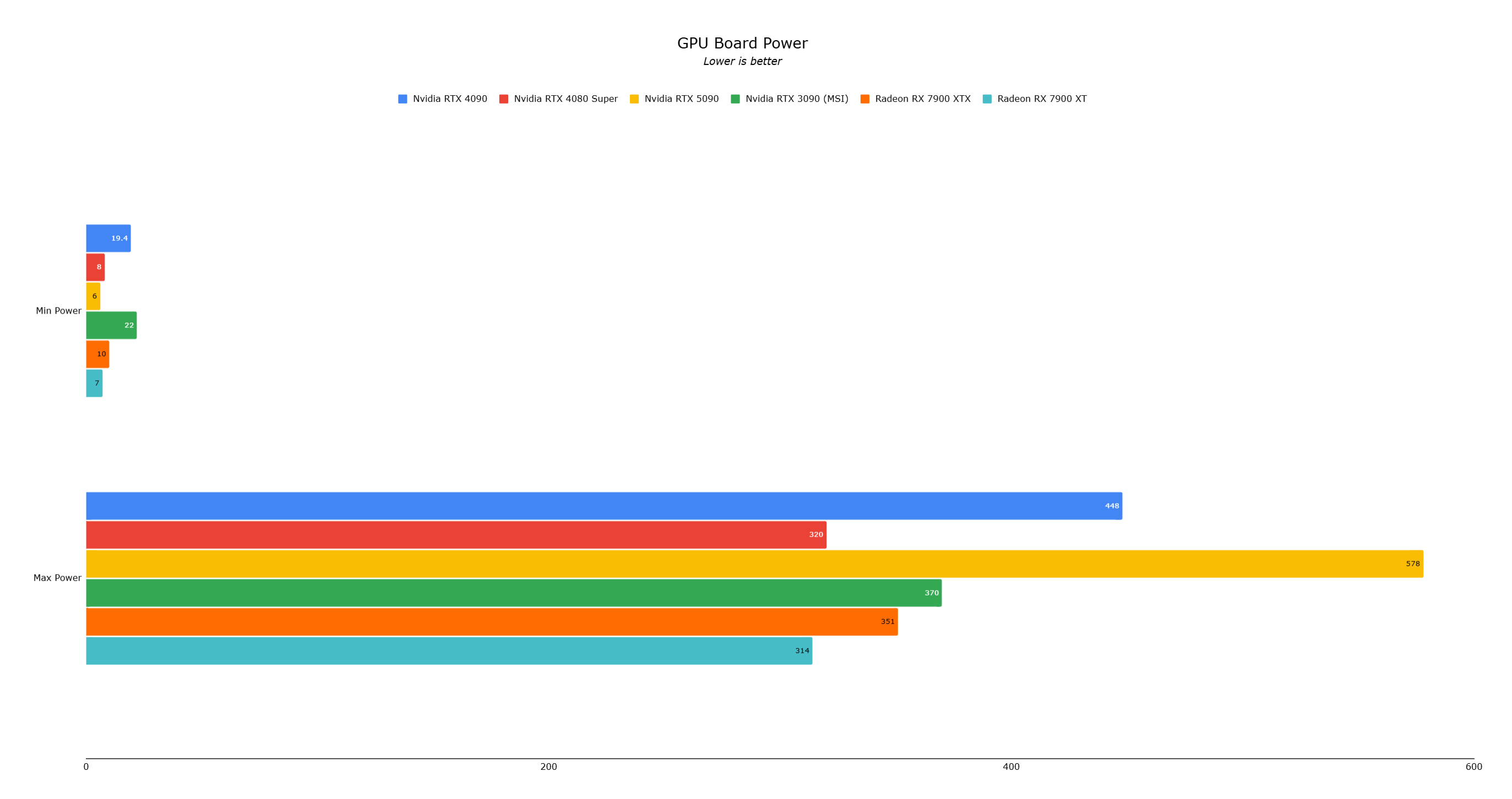
This powerful silicon is paired with 32GB of GDDR7 VRAM, a generational leap from the RTX 4090's GDDR6X. While faster and more power-efficient, the 5090's 575W power draw (a significant increase over the 4090) shows power efficiency isn't the primary focus.
The improved Tensor Cores enable a shift to a Transformer Neural Network (TNN) for the DLSS algorithm, instead of a Convolutional Neural Network (CNN). While frame rate might not improve significantly with DLSS enabled, Nvidia claims image quality increases, reducing artifacts like ghosting.
Beyond the internal DLSS changes, Nvidia introduces Multi-Frame Generation. This enhanced Frame Gen technology is more efficient and smoother, generating multiple frames from each rendered image. This drastically improves frame rates but should be used only with already decent frame rates, similar to the previous generation.
Purchasing Guide
The Nvidia GeForce RTX 5090 launches January 30th, starting at $1,999 (Founders Edition). Third-party cards will likely be more expensive.
The Founders Edition
The RTX 5090's 575W power draw (much higher than the RTX 4090's 450W) generates more heat, demanding robust cooling. While expecting a larger card, Nvidia surprisingly created a smaller, dual-slot design with dual fans.

During testing (including standard benchmarks and DLSS 4 with multi-frame generation), temperatures peaked around 86°C at 578W power consumption. While high (higher than the RTX 4090's 80°C), it's not high enough to cause throttling.
Nvidia achieved this by centrally positioning a compact PCB, with fans on either side and a heatsink spanning the card's width. Air intake is from the bottom, expelled through the top, eliminating rear exhaust vents unlike previous generations.
The design maintains a similar aesthetic to previous generations, featuring a silver 'X' and a lit 'GeForce RTX' logo.

The power connector, while resembling the 12VHPWR connector, is a new 12V-2x6 connector, claimed to be more efficient. An included adapter uses four 8-pin PCIe power connectors. The angled connector on the card improves cable connection.
This design allows for smaller PC builds, unlike previous generations. However, third-party cards will likely be larger.
DLSS 4: Fake Frames?
Nvidia claims up to 8x performance boosts, though reality is less dramatic. The RTX 5090 delivers extremely high frame rates in demanding games, largely due to frame generation. While raw rasterization performance improves, the real advantage lies in generating extra frames.
DLSS 4's 'Multi-Frame Generation' builds upon DLSS 3's Frame Generation, but it's more efficient. A new AI Management Processor (AMP) core efficiently assigns tasks across the GPU, traditionally handled by the CPU.
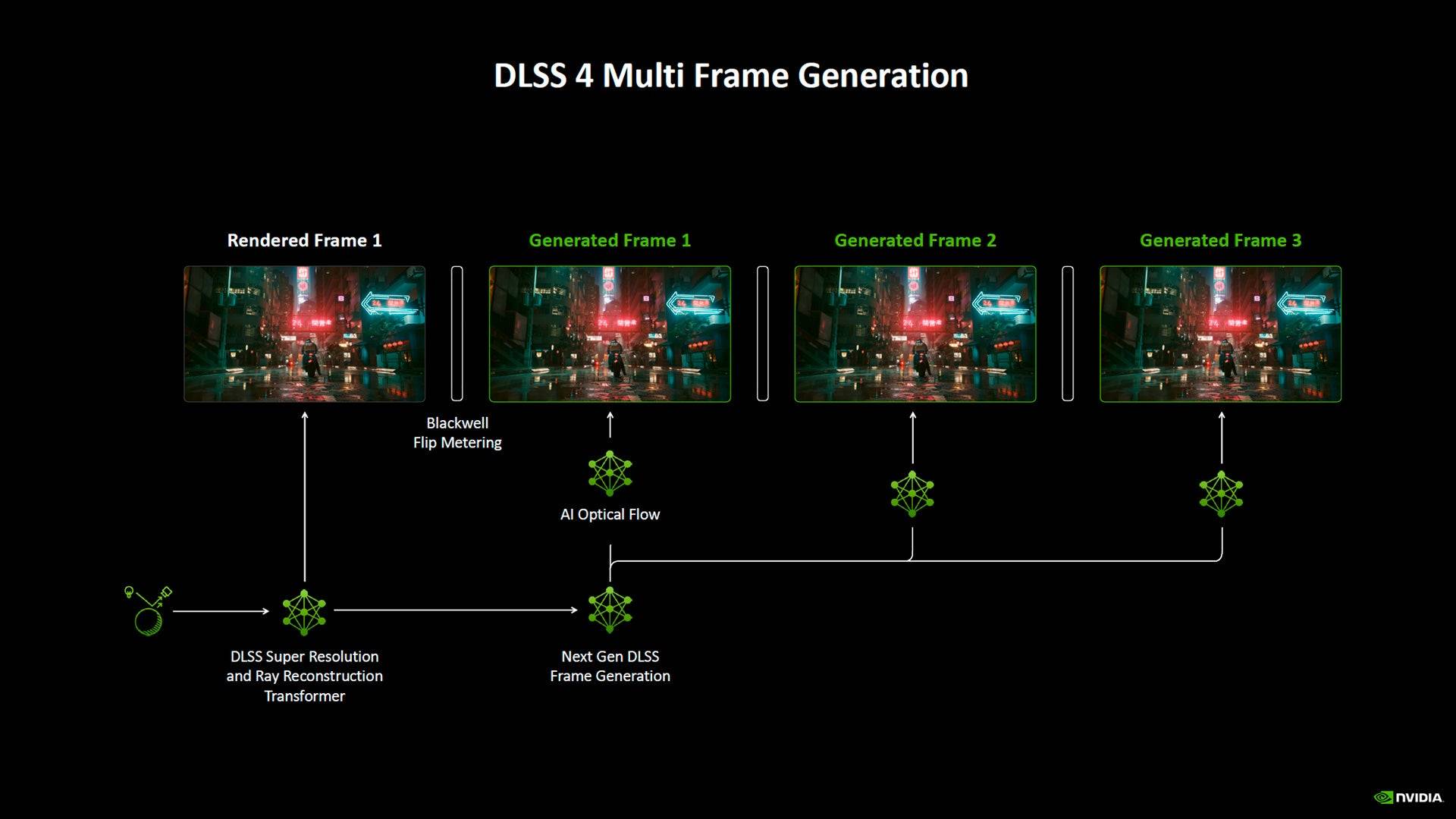
Nvidia states the AMP and 5th-gen Tensor Cores create a 40% faster frame generation model using 30% less memory. It generates three AI frames per rendered frame, using a Flip Metering algorithm to minimize input lag. This explains why it doesn't work on RTX 4000 cards, as their frame generation relied on the CPU, introducing more latency.
This isn't a magic fix; it's best used with already acceptable frame rates (around 60fps without Frame Gen). Enabling it with low frame rates causes significant latency. Pairing it with DLSS upscaling maximizes performance.
At launch, DLSS 4 will support many DLSS 3 Frame Generation games. Testing was limited to beta builds of Cyberpunk 2077 and Star Wars Outlaws.

In Cyberpunk 2077 at 4K with Ray Tracing Overdrive and DLSS Performance, the RTX 5090 achieved 94fps. DLSS 2x frame generation increased this to 162fps, and 4x frame generation reached 286fps (exceeding the display's capabilities). Star Wars Outlaws showed similar results, reaching around 300fps with DLSS 4.
Multi-Frame Generation works surprisingly well, with minimal noticeable artifacts. High-end 4K displays are needed to fully benefit. While 75 games will support DLSS 4 at launch, flawless performance in every game isn't guaranteed.
RTX 5090 – Performance
The RTX 5090 is incredibly powerful, but testing revealed complexities. 3DMark showed generational improvements over the RTX 4090. However, in most games, the RTX 5090 was CPU-bottlenecked at 4K, even with the Ryzen 7 9800X3D. Upgrading from a high-end card might not yield significant improvements for many users. This card is an investment in future games.
DLSS 4 was disabled in comparative benchmarks, using public drivers (Nvidia 566.36, AMD Adrenalin 24.12.1) and latest game builds.
Test System:
- CPU: AMD Ryzen 7 9800X3D
- Motherboard: Asus ROG Crosshair X870E Hero
- RAM: 32GB G.Skill Trident Z5 Neo @ 6,000MHz
- SSD: 4TB Samsung 990 Pro
- CPU Cooler: Asus ROG Ryujin III 360
In 3DMark, the RTX 5090 was up to 42% faster than the RTX 4090 (Speed Way: 14,399 vs 10,130; Port Royal: 36,946 vs 25,997). Compared to the RTX 3090, the improvement is even more dramatic (2.5x). Real-world gaming performance differs.
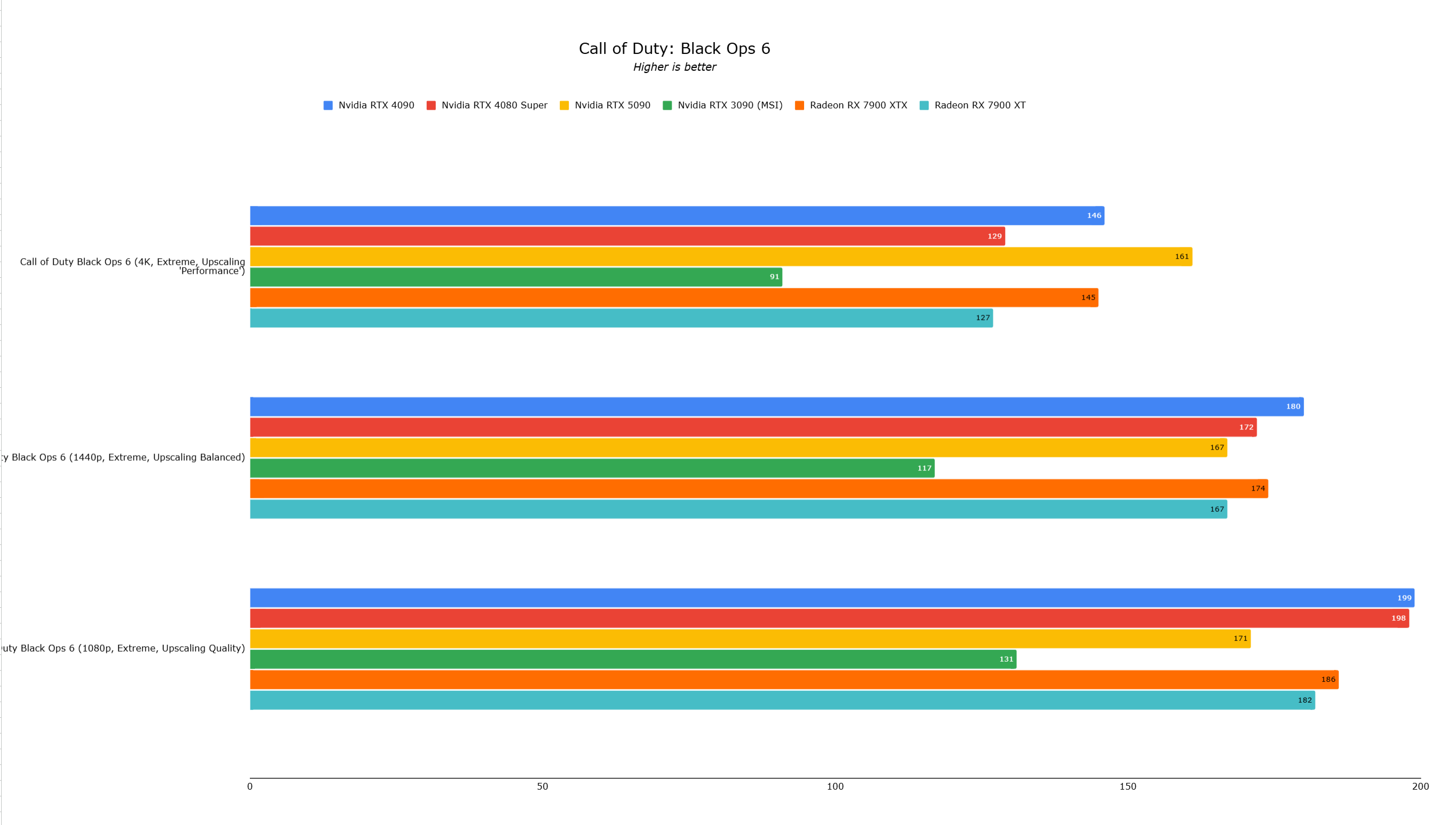
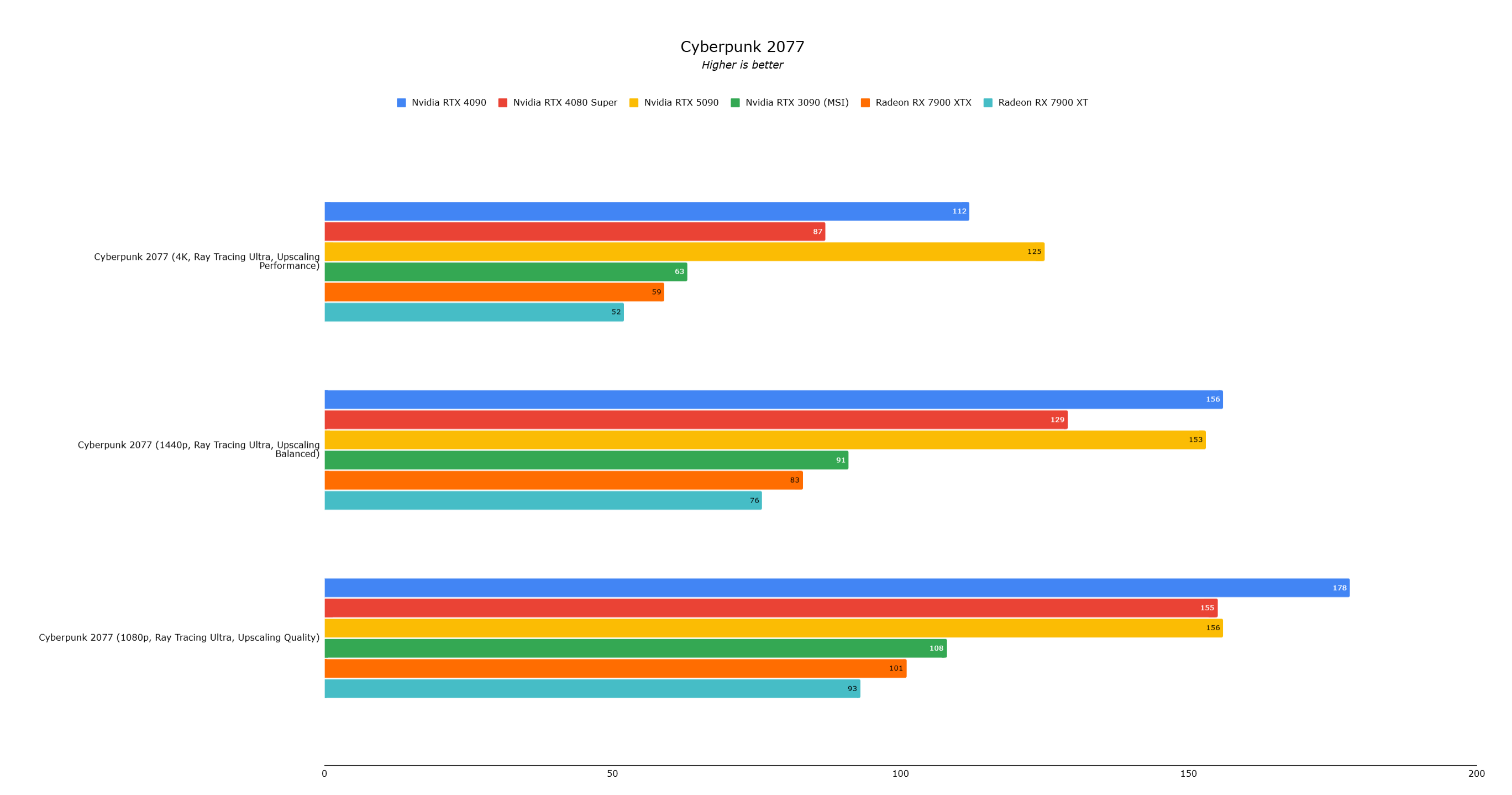
Call of Duty Black Ops 6 showed CPU bottlenecking at 4K (RTX 5090: 161fps, RTX 4090: 146fps—a 10% difference). Cyberpunk 2077 showed a similar 10% improvement. Lower resolutions showed less scaling.
Metro Exodus: Enhanced Edition (DLSS disabled) demonstrated a 25% improvement over the RTX 4090 at 4K Extreme.
Red Dead Redemption 2 showed only a 6% improvement at 4K max settings.
Total War: Warhammer 3 (no ray tracing or upscaling) showed a 35% improvement, closer to 3DMark results.
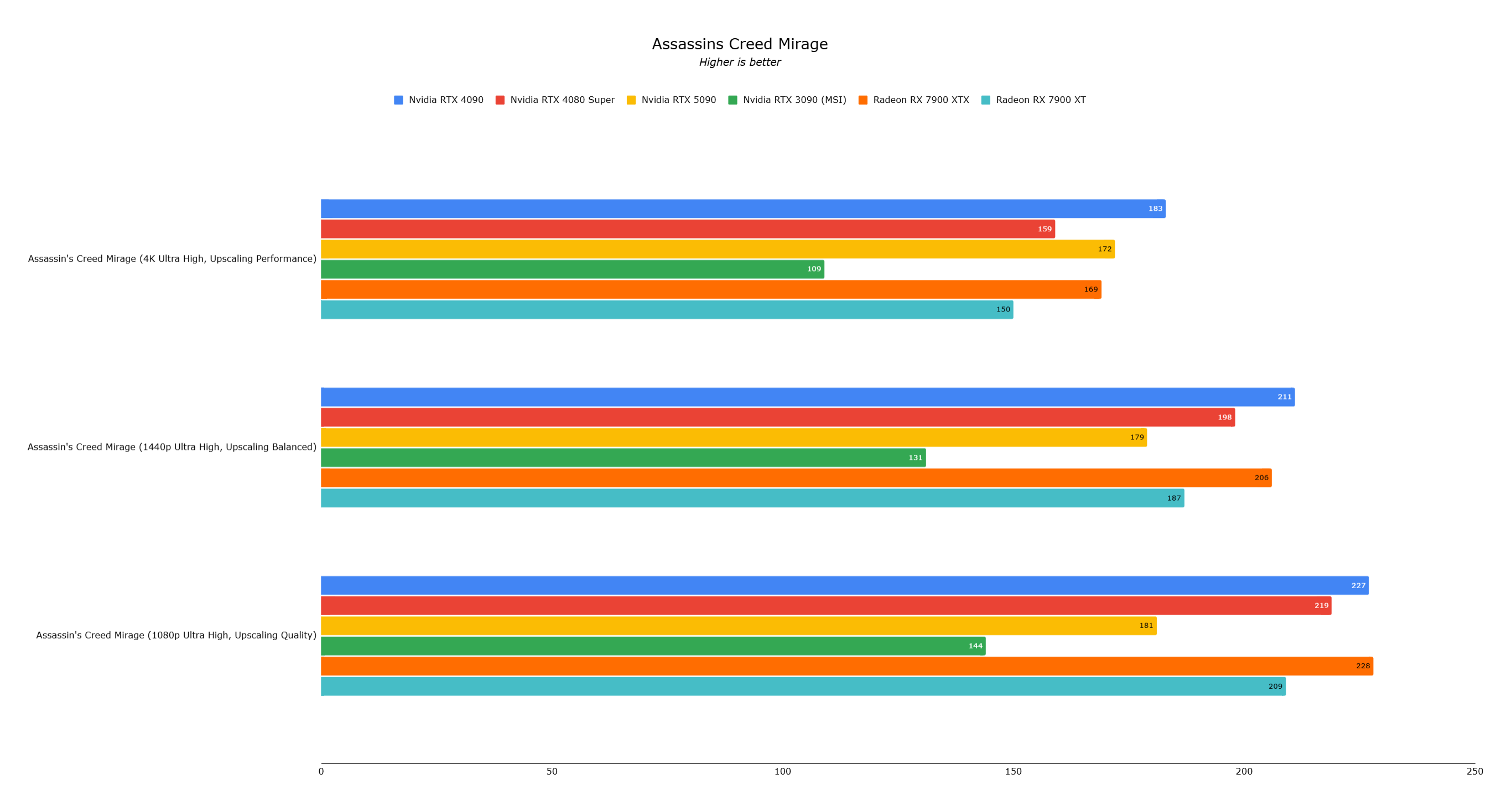
Assassin's Creed Mirage showed lower performance than the RTX 4090, likely a driver issue.
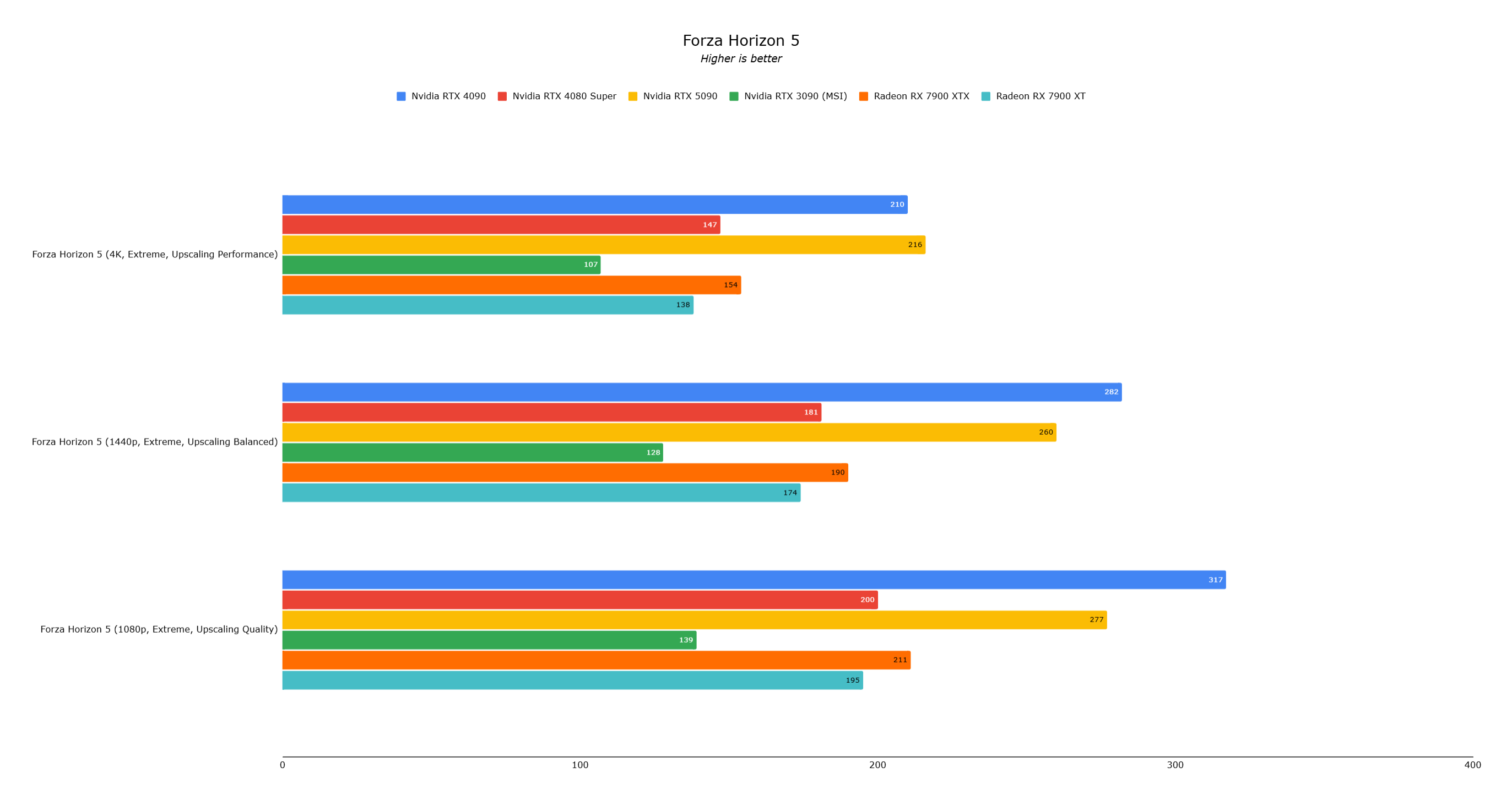
Black Myth: Wukong showed a 20% improvement. Forza Horizon 5 showed negligible differences.
The RTX 5090 is the fastest consumer GPU, but many games don't fully utilize its power. This will change over time, but current owners of RTX 4090 might not see a compelling upgrade.
The RTX 5090 focuses on AI-powered gaming. DLSS 4 significantly boosts frame rates, appealing to cutting-edge gamers willing to invest. For others, the RTX 4090 remains powerful enough.
AnswerSee Results
-
RuneScape's April Developer Diary has arrived, detailing the latest update: "Return to the Desert: Pharaoh's Folly." This brand-new quest launches today and will be available until April 28th. Your mission is to survive the treacherous Shifting TombsAuthor : Andrew Mar 12,2026
-
Firaxis Games, the developer behind Civilization VII, has laid off an unspecified number of staff today. This comes despite Take-Two Interactive CEO Strauss Zelnick's recent comments that the game's sales are meeting the company's projections.MultiplAuthor : Joshua Mar 12,2026
-
 Kitty LetterDownload
Kitty LetterDownload -
 SwingShotDownload
SwingShotDownload -
 The Seven Realms 3Download
The Seven Realms 3Download -
 Curse of the Night Stalker - Chapter 3 releaseDownload
Curse of the Night Stalker - Chapter 3 releaseDownload -
 My Home Design: My House GamesDownload
My Home Design: My House GamesDownload -
 100+ RiddlesDownload
100+ RiddlesDownload -
 Elite PokerDownload
Elite PokerDownload -
 Sinful Summer: A Tale of ForbiddenDownload
Sinful Summer: A Tale of ForbiddenDownload -
 Monster Girl 1000Download
Monster Girl 1000Download -
 1-19 Number GameDownload
1-19 Number GameDownload
- HoYo Fest 2025: Fresh Updates on Comeback
- Mastering Two-Handed Weapons in Elden Ring: A Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Shinigami Progression in Hollow Era
- Roblox Simulator Codes: Unlock Exclusive Rewards!
- Wuthering Waves: Uncover the Secrets of Whisperwind Haven's Palette
- Top 25 Palworld Mods to Enhance Your Game